Creating Projects
30/09/2025
To be able to create and manage taxonomies in PoolParty you have to create a project which will be then managed in the Thesaurus Manager.
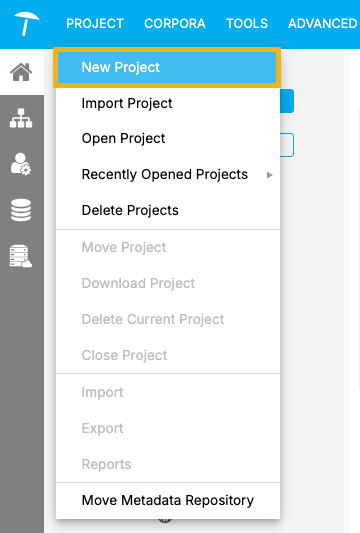
In the PROJECT menu, select New Project to create a new project.
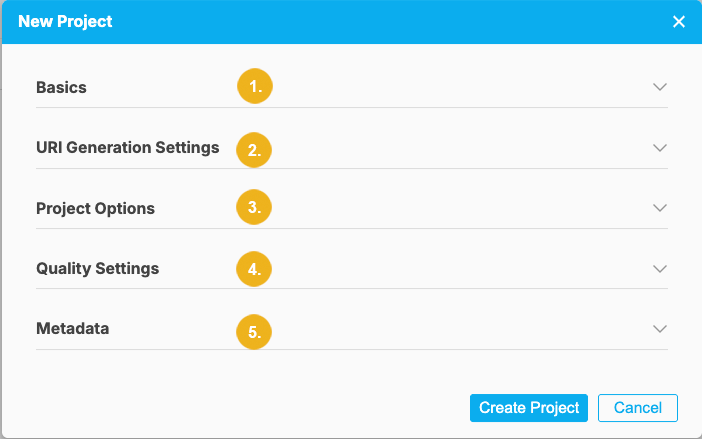
The New Project dialog opens where you can enter information in five different sections:
Tip
All mandatory input fields are marked by a trailing asterisk.
Note
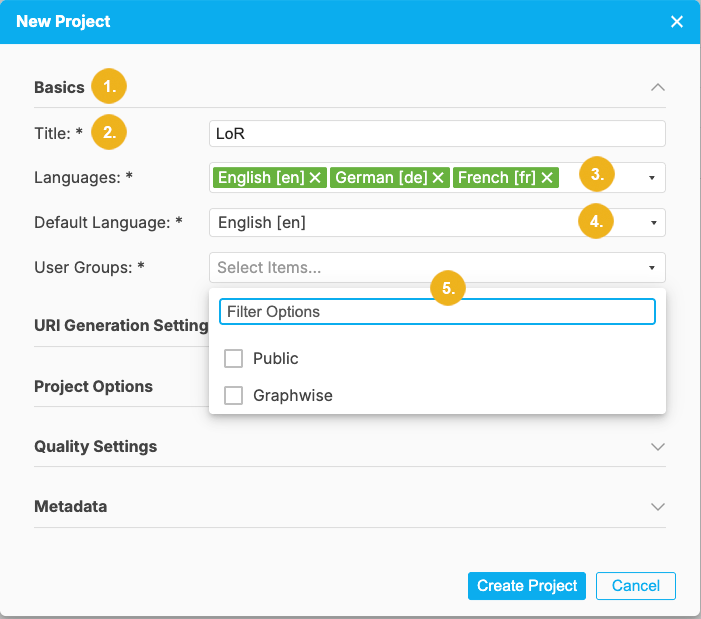
When you click on the arrow on the right pointing down you can access any of the five groups of settings for the new project. The Basics section is always open by default when you click on the New Project menu item.
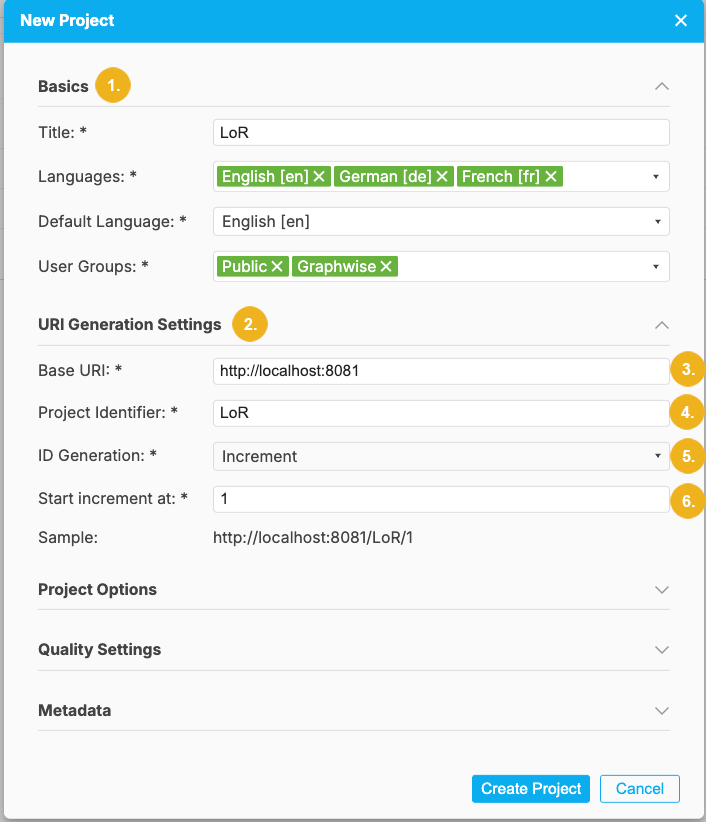
Basics (1) - contains mandatory fields: Title, Languages, Default Language and User Groups
URI Generation (2) - the following mandatory settings are configured in this section: Base URI, Project Identifier, ID Generation, the starting increment for the ID generation. At the end of this section you see the sample of the URI.
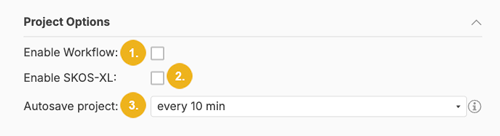
Project Options (3) - this section is comprised of two checkboxes - Enable Workflow and Enable SKOS-XL and a pulldown called Autosave project.
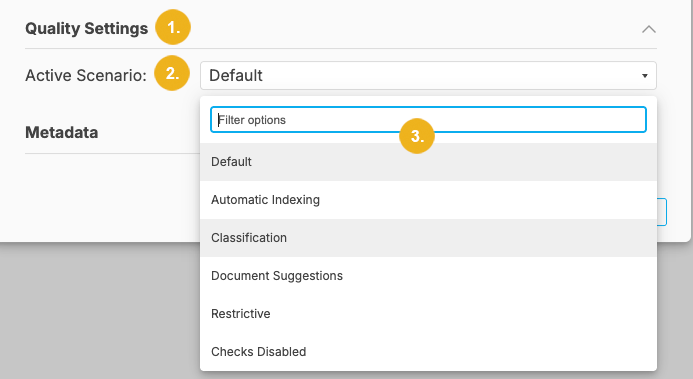
Quality Settings (4) - here you can select an Active Scenario to be used for your project.
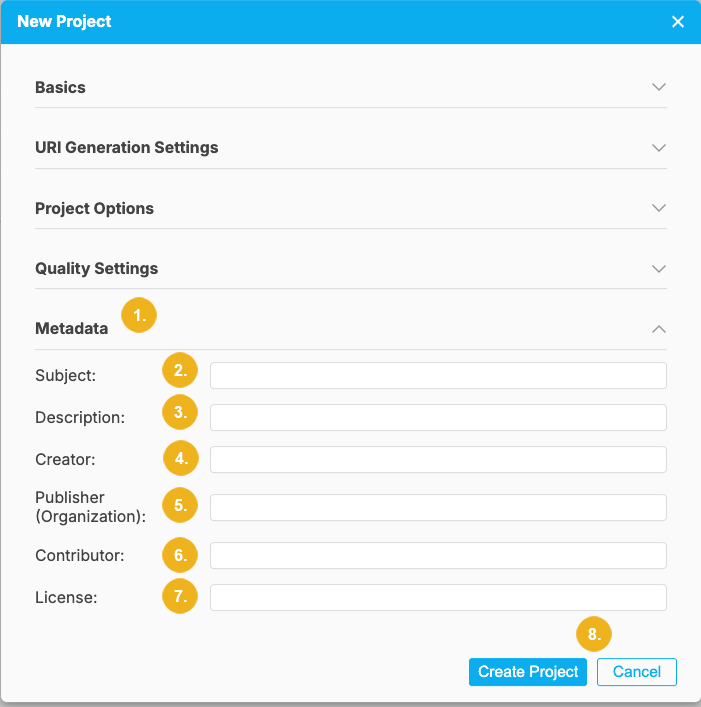
Metadata (5) is the last section containing the following fields: Subject, Description, Creator, Publisher (Organization), Contributor and License.
After having specified all mandatory details and desired optional information click on the Create Project button on the bottom of this dialog window or on Cancel to abort the operation and discard all inputs.
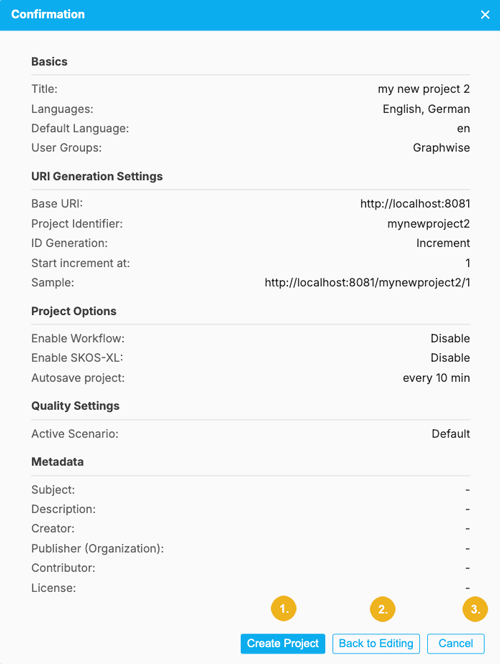
After clicking the Create Project button a new window opens showing all the details you have specified for your new project. At the bottom of this Confirmation window are three buttons:
Create Project (1) - if all details shown in this window are correct and you want to create this new project click this button.
Back to Editing (2) - if you want to change any of the details and settings, use this button to return to the previous dialog.
Cancel (3) - click this button to cancel the operation and discard all inputs.